The sample is selected because they are convenient. Quantitative Research Design Methods Topics Types of quantitative research Measurement Fundamentals Concepts and construct validity Levels of measurement Research Validity Quantitative Research Measurement Fundamentals A key difference is that normal science deals with concepts that are well defined and to great extent standardized measures eg.

Lecture Notes On Research Methodology Ppt Download
From the target population and the estimation technique.

. A brief mention of the important sample designs is as follows. Thus in a proposal the procedures need to be identified within the design. Deliberate sampling is also known as purposive or non-probability sampling.
Another option is probability-proportional-to-size PPS sampling in which the selection probability for each element is set to be proportional to its size measure up to a maximum of 1. Department of Anesthesia Critical Care and Pain Medicine Massachusetts General Hospital. In a broad context survey researchers are interested in obtaining some type of information through a survey for some population or universe of interest.
A complete enumeration of all the items in the population is known as a census inquiry. TYPES OF SAMPLING There are main two types of sampling based on chances of being selected or not selected the population unit into the sample. Data analysis in mixed methods research relates to the type of research strategy chosen for the procedures.
Nonprobability sampling or judgment sampling depends on subjective judgment. Salant p62 The nonprobability method of sampling is a process where probabilities cannot be assigned to the units objectively and hence it becomes difficult to determine the reliability of the sample results in terms of probability. A sample is a subset of a population.
Flipping a coin The more times we flip a coin the more likely. Sample - the actual participants in the study representative of the population Types of Research Designs Experimental research Correlational research Surveys questionnaires Observations Case Studies The Experiment Only type of study that allows for statement of cause and effect Experimenter has degree of control over key variables not possible in other research designs. Example Research Designs Quantitative Correlational -Explanatory design.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Business Research Methods Week 3 29 August 2005 MBA III Research Methodology Course Instructor. The Research Design The research design is the actual structure or framework that indicates a the time frames in which data will be collected b when the intervention will be implemented or not and c how many groups will be involved Edmonds Kennedy 2012. 8 PROBABILITY SAMPLING Probability sampling is one in which every unit of the population has an equal probability chance of being selected for the sample.
Political polls Generalize about a larger population. Selecting the right people Have to be selected scientifically so that they are representative of. Samples are drawn through a systematic procedure called a sampling method.
Download Full PDF Package. Probability sampling is based on the concept of random selection whereas non. Decide on your data analysis strategies.
A sample design is the framework or road map that serves as the basis for the selection of a survey sample and affects many other important aspects of a survey as well. Sample statistics measure characteristics of the sample to estimate the value of population parameters that describe the characteristics of a population. All the items under consideration in any field of inquiry constitute a universe or population.
The process of obtaining information from a subset sample of a larger group population The results for the sample are then used to make estimates of the larger group Faster and cheaper than asking the entire population Two keys 1. A single person or 50 people The larger the sample the more likely the sample will share the same characteristics as the population EXAMPLE. SAMPLING METHODS Chapter 4 A sample is a subgroup of elements from a population Can be any size EXAMPLE.
Often used during preliminary research efforts to get an estimate without incurring the cost or time required to select a random sample Judgment Sampling Judgment sampling is a common nonprobability method. Sample design refers to the plans and methods to be followed in se lecting sample. A short summary of this paper.
Identify your population and sampling method. 47 Disproportionate Stratified Sample Stratified Random Sampling Stratified random sample A method of sampling obtained by 1 dividing the population into subgroups based on one or more variables central to our analysis and 2 then drawing a simple random sample from each of the subgroups Reduces cost of research eg. In most situations the output of a survey conducted with a non-probable sample leads to skewed results which may not represent the desired target population.
State the objectives of the survey Define the target population Define the data to be collected Define the variables to be determined Define the required precision accuracy Define the measurement instrument Define the sample size sampling method then select the sample Sampling Distributions. Choose your data collection methods. Frequently asked questions about research design.
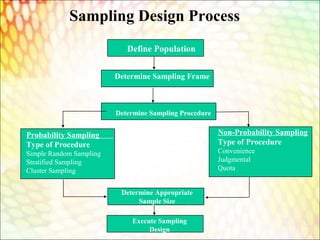
The non-probability method is a sampling method that involves a collection of feedback based on a researcher or statisticians sample selection capabilities and not on a fixed selection process. Choose a type of research design. Types of sampling design in Research Methodology.
The sample is selected based upon judgment. When you form a sample you often show it by a. There are two types of sampling methods.
Non-probability sampling involves non-random selection based on convenience or other criteria allowing you to easily collect data. Probability sampling involves random selection allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group. In a simple PPS design these selection probabilities can then.
Consider your aims and approach. Plan your data collection procedures. However analysis occurs both within the quantitative descriptive and inferential numeric analysis approach and the qualitative description and thematic.
MGT629 Business Research Methods Module 6 f Sampling Terminology Sample Population or universe Population element Census f Sampling Methods Simple random sampling Stratified random sampling Cluster sampling 3 fPopulation Any complete group People Sales territories Stores Sample Subset of a. Populations and Samples A population would be the first choice for analysis. On the representation basis the sample may be probability sampling or it may be non-probability sampling.
There are different types of sample designs based on two factors viz the representation basis and the element selection technique. It is a nonprobability method.

Types Of Sampling Design In Research Methodology Datapott Analytics

Research Methodology Lecture No 14 Sampling Design Ppt Download





0 comments
Post a Comment